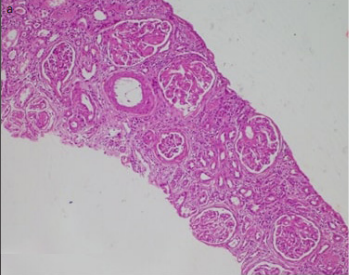
Light chain deposition disease (LCDD) is a rare disease and the most common subtype of monoclonal immunglobulin deposition disease (MCDD). The most commonly affected organ is the kidney, characterized by nodular glomerulosclerosis and proteinuria at the nephrotic level. The LCDD is often associated with underlying plasma cell dyscrasias or lymphoproliferative diseases. The investigation of the underlying disease is very important for the treatment. We herein present a case of nodular glomerulosclerosis with nephrotic syndrome—a case of a 53-year-old woman who presented with acute renal failure with no previously known disease and was diagnosed with rarely seen LCDD, and whose subsequent examinations revealed a plasma cell neoplasm.
Cite this article as: Ergen P, Yuyucu Karabulut Y, Kıykım AA, Ballı E, Köse EÇ. Light Chain Deposition Disease Diagnosed with Renal Biopsy: A Case Report. Turk J Nephrol 2019; 28(4): 331-4.

.png)


.png)

.png)