Objective: Renal biopsy plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and treatment of renal diseases. The aim of the present study was to review the reasons leading to biopsy and the pathological diagnoses and to investigate the effectiveness and safety of ultrasound-guided percutaneous renal biopsy in children.
Materials and methods: A total of 410 renal biopsies performed in 362 patients between January 2007 and January 2018 at Dr. Sami Ulus Maternity and Child Health and Diseases Training and Research Hospital, Department of Pediatric Nephrology and Rheumatology were retrospectively reviewed. Pathology specimens were evaluated by light and immunofluorescence microscopy. Electron microscopy was performed only on specific occasions.
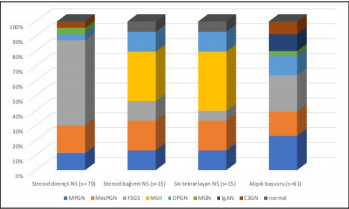
Results: The mean age of the patients was 10.1±4.4 years, and 55.2% were males. Nephrotic syndrome (44.5%) was the most common indication for renal biopsy. Hematuria±proteinuria (19.9%), acute renal injury (15.7%), chronic renal disease (3.2%), and complex renal manifestations (16.6%) were the following indications. The overall complication rate was 8%, and the most common of which was perirenal hematoma (7.5%). The most common histopathological diagnosis was primary glomerulopathy (56.6%). Among primary glomerulopathies, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis was the leading diagnosis (16.5%), followed by mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis (7.7%) and IgA nephropathy (7.7%). The second most common histological diagnosis was manifestations secondary to systemic diseases (30.9%), among which Henoch-Schönlein purpura (12.4%) and lupus (9.1%) were the leading causes.
Conclusion: Renal biopsy is a safe and effective procedure in the diagnosis and treatment of childhood kidney diseases.
Cite this article as: Kargın Çakıcı E, Yazılıtaş F, Üner Ç, Can G, Kurt-Şükür ED, Güngör T, et al. Indications and Outcomes of Renal Biopsies in Children: A Single-Center 12-Year Experience. Turk J Nephrol 2019; 28(4): 250-6.

.png)


.png)

.png)